It was a little hard to understand the problem. I could see and understand the picture of the example, and it didn’t take very long to write the code. As you can see from solving the problem, there is a cute trick hidden in the problem. It’s a tiny trick that gives you the fear of being a complicated problem before you write the code. (*´o`*)
1. Problem
We have a wooden plank of the length n units.
Some ants are walking on the plank, each ant moves with speed 1 unit per second.
Some of the ants move to the left, the other move to the right.
When two ants moving in two different directions meet at some point,
they change their directions and continue moving again.
Assume changing directions doesn’t take any additional time.
When an ant reaches one end of the plank at a time t, it falls out of the plank imediately.
Given an integer n and two integer arrays left and right, the positions of the ants moving to the left and the right. Return the moment when the last ant(s) fall out of the plank.
Example1 :
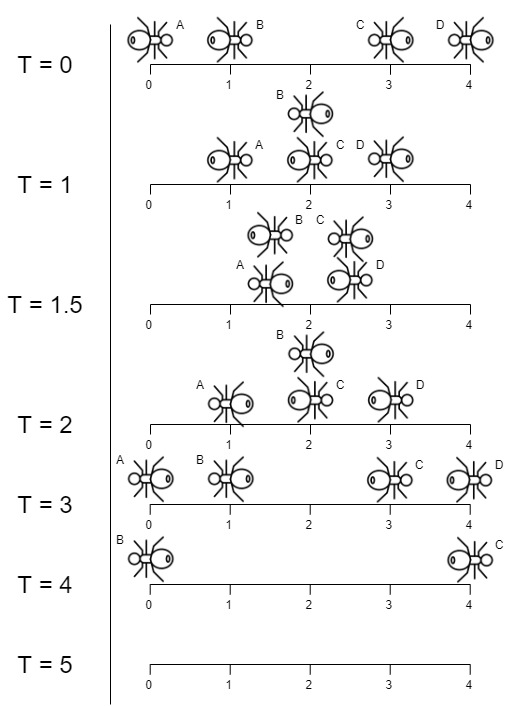
Input: n = 4, left = [4,3], right = [0,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: In the image above:
- The ant at index 0 is named A and going to the right.
- The ant at index 1 is named B and going to the right.
- The ant at index 3 is named C and going to the left.
- The ant at index 4 is named D and going to the left.
Note that the last moment when an ant was on the plank is t = 4 second, after that it falls imediately out of the plank. (i.e. We can say that at t = 4.0000000001, there is no ants on the plank).
Example2 :
Input: n = 7, left = [], right = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: 7
Explanation: All ants are going to the right, the ant at index 0 needs 7 seconds to fall.
Constraints
- 1 <= n <= 10^4
- 0 <= left.length <= n + 1
- 0 <= left[i] <= n
- 0 <= right.length <= n + 1
- 0 <= right[i] <= n
- 1 <= left.length + right.length <= n + 1
- All values of left and right are unique, and each value can appear only in one of the two arrays.
2. Thinking Algorithm
- Sort the
leftandrightvector received by parameter.
(leftis descending order,rightis ascending order) - Consider the ants at the end of a plank from the beginning and drop them off.
- Repeat the following while both
leftandrightsizes are not zero. - Increase the
answervar, decrease the elements inleftvector and increase inrightvector.
(answer: time (seconds), decreasing inleft: ants move left, increasing inright: ants move right) - If there is an ant at the end of the plank, drop(pop) it.
- After the repeat statement (while loop) is complete, if the
leftandrightvectors are not empty,
increase theanwerby the position of the last ant in each direction. - Returns
answervar.
3. Solution
[C++]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class Solution {
public:
int getLastMoment(int n, vector<int>& left, vector<int>& right) {
int answer = 0;
sort(left.begin(), left.end(), greater<int>());
sort(right.begin(), right.end());
if(left.size() != 0 && left.back() == 0) left.pop_back();
if(right.size() != 0 && right.back() == n) right.pop_back();
while(left.size() != 0 && right.size() != 0) {
answer++;
for(int i = 0; i < left.size(); i++) left[i]--;
for(int i = 0; i < right.size(); i++) right[i]++;
if(left.back() == 0) left.pop_back();
if(right.back() == n) right.pop_back();
}
if (left.size() != 0) answer += left.front();
else if (right.size() != 0) answer += n - right.front();
return answer;
}
};
4. To Think Deeper
- A cute trick in which the left and right ants change direction when they encounter each other
- You have to think of the ants at the end of a plank from the beginning (at the moment, T = 0)
5. Reference ٩( ᐛ )و
- Nothing ¯\(ツ)/¯
1
출처: LeetCode Contest, https://leetcode.com/contest/